
The BRCA 1/2 gene regions are analyzed for the presence of pathogenic and likely pathogenic mutations. The Strand HRD test is an NGS test that sequences BRCA1/2 genes and tens of thousands of loci across the genome. Thus, determining HRD Status leads to more positive outcomes for people diagnosed with Ovarian Cancers

If found positive, it helps clinicians propose a therapy - PARP (poly ADP-ribose) inhibitors - a relatively new targeted frontline therapy as a potential approach with higher rates of success. The Strand HRD Panel checks if a patient is HRD positive (they have deficiency in DNA repair mechanism). Chromosomal instability leads to Genomic Scars which affects the body's DNA Repair mechanism (HRR) with gene mutation. It is a "Genomic Instability Score Card", which helps physicians take informed decison on treatment methods for cancers, especially ovarian cancer.
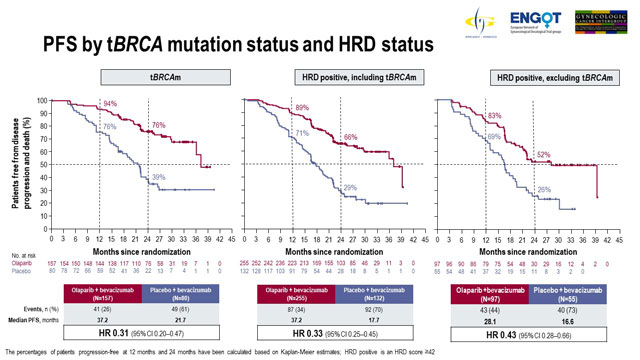
HRD generates certain permanent changes in the genome known as ‘Genomic scars’. Besides ovarian cancer, HRD may be found in other cancers, including breast, pancreatic and prostate cancer. Determining HRD status leads to selection of more patients who benefit from PARPi therapy. The European Commission has approved Lynparza (olaparib), in combination with bevacizumab, as a first-line maintenance therapy for women with advanced ovarian cancer positive for homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) and who responded to platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients who are HRD positive respond well to PARPi (poly ADP-ribose inhibitors), a relatively new targeted frontline therapy. Up to 50% of women with advanced ovarian cancer have HRD positive cancer cells. 1: Frontline Treatments in Ovarian Cancer. Treatment of HRD-Negative Ovarian Cancer. This functional defects in Homologous Recombination Repair mechanisms is known as Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD). Advanced Ovarian Cancer: New Perspectives on Systemic Therapy - Episode 11. When the functionality of these genes are lost, it results in DNA double strand breaks, which persists and causes complete damage of DNA at that site, and subsequent repair by nonhomologous end-joining, a low-fidelity repair pathway that introduces inversions and other genomic aberrations. The most prominent genes involved in Homologous Recombination Repair are BRCA1 and BRCA2 along with other genes such as RAD51, ATM/ATR, CDK12 -complex, etc. In the human body, the primary mechanism of repairing DNA double-strand breaks is Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR).






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
